7 Fascinating Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt, known for its captivating legacy, was predominantly shaped by the mighty Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt. These powerful monarchs, iconic in their rule, left an indelible mark on history, shaping civilizations and leaving legacies that endure through the ages. Let’s delve into the lives of seven of the most fascinating Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt, exploring their contributions, reigns, and enduring influence.
Table of Contents
1. Khufu (2589-2566 BCE)
The Great Pyramid Builder

Khufu, the second Pharaoh of the Fourth Dynasty, is renowned for commissioning the construction of the Great Pyramid of Giza, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. His reign witnessed remarkable architectural achievements, with the Great Pyramid standing as a testament to his vision, wealth, and engineering prowess.
During his reign, Khufu’s focus on monumental construction projects not only included the Great Pyramid but also involved significant infrastructure enhancements across Egypt. His administration oversaw the development of irrigation systems, facilitating agricultural growth and prosperity for the kingdom’s inhabitants. Khufu’s efforts in urban planning and infrastructure laid the foundation for Egypt’s structural advancements.
2. Tutankhamun (1332-1323 BCE)
The Boy King
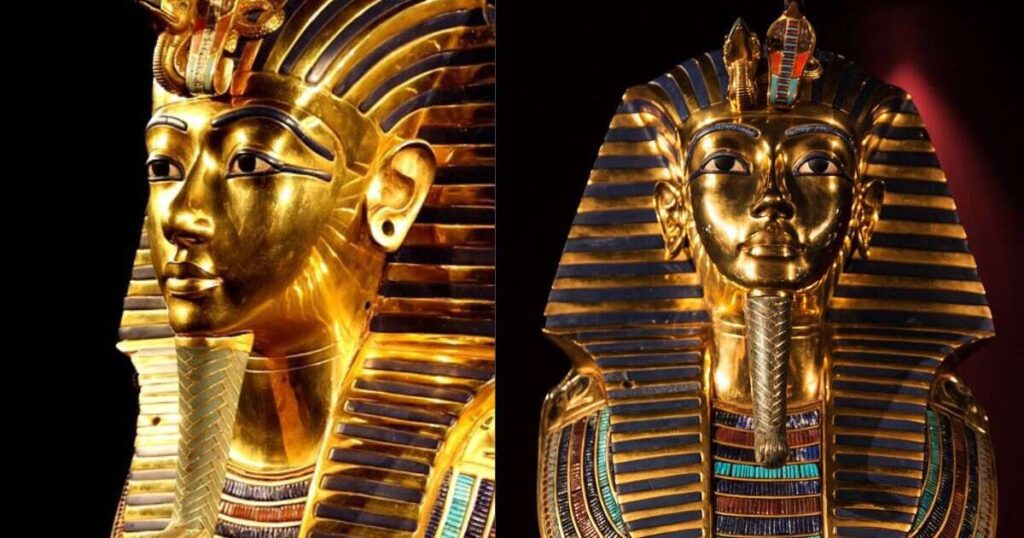


Tutankhamun, often referred to as the “Boy King,” ascended to the throne at a tender age (9 years) and ruled during the 18th dynasty. His tomb, discovered nearly intact by archaeologist Howard Carter in 1922, revealed an astonishing array of artifacts, including his iconic gold mask. Despite his brief rule, Tutankhamun’s legacy remains unparalleled, offering invaluable insights into ancient Egyptian culture and customs.
Aside from his famous tomb, Tutankhamun’s reign saw a revival of traditional religious practices and artistic endeavors. He played a role in reinstating worship of old gods and revitalizing temples previously neglected, aiming to restore Egypt’s spiritual balance. His reign was marked by a cultural resurgence, with a renewed emphasis on traditional rituals and art.
3. Hatshepsut (1478-1458 BCE)
The Female Pharaoh
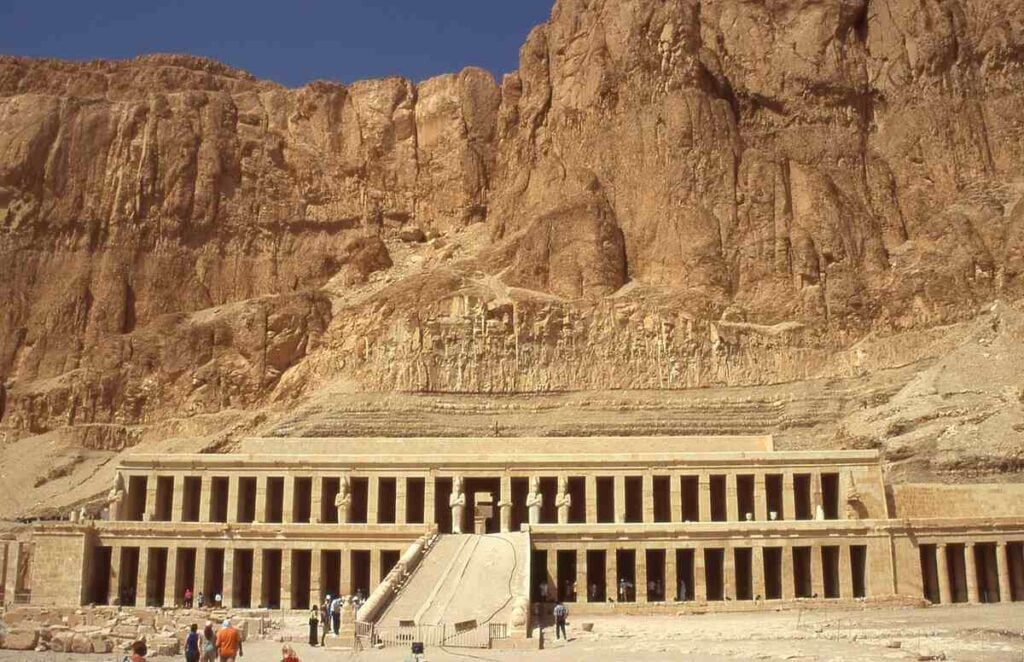


Hatshepsut defied conventions by becoming one of the few female Pharaohs in Egyptian history. As the fifth pharaoh of the 18th dynasty, she wielded remarkable power and oversaw a prosperous era marked by trade expeditions and ambitious construction projects, including the magnificent mortuary temple at Deir el-Bahri. Her reign symbolized strength and stability, leaving an indelible mark on Egypt’s historical landscape.
In addition to her grand construction projects, Hatshepsut’s reign fostered economic prosperity and cultural flourishing. She initiated trading expeditions to the Land of Punt, establishing robust trade networks that brought exotic goods like myrrh, gold, and ivory to Egypt. These trading ventures bolstered Egypt’s economy, promoting cultural exchange and affluence throughout the kingdom.
4. Ramesses II (1279-1213 BCE)
The Mighty Pharaoh
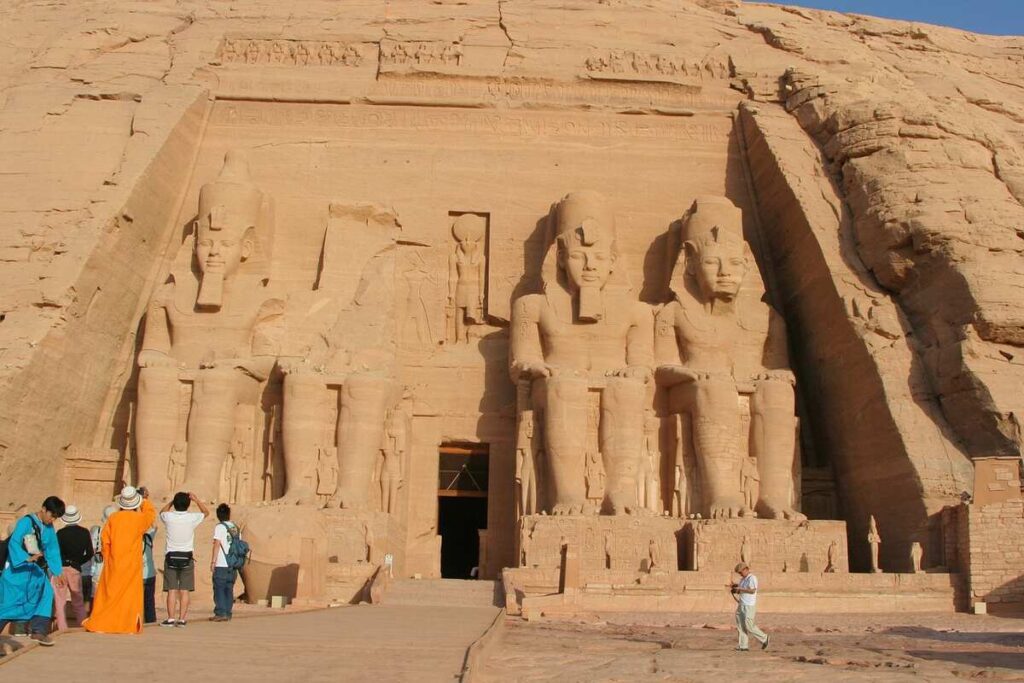


Ramesses II, also known as Ramesses the Great, boasted an extraordinary reign spanning an unprecedented 66 years during the 19th dynasty. Renowned for his military prowess and diplomatic acumen, he left an enduring legacy through monumental building projects, including the awe-inspiring temples of Abu Simbel and the grand Ramesseum. His leadership and achievements solidified his place as one of Egypt’s most influential and celebrated Pharaohs.
Beyond his architectural marvels, Ramesses II’s reign was characterized by an era of significant international diplomacy and strategic alliances. He negotiated peace treaties with rival kingdoms, fostering stability in the region. Additionally, his military campaigns expanded Egypt’s borders, securing dominance and contributing to an era of relative peace and prosperity within the kingdom.
5. Cleopatra VII (51-30 BCE)
The Last Pharaoh


Cleopatra VII, the final ruler of the Ptolemaic Kingdom, remains an iconic figure in history and popular culture. Her intelligence, charm, and strategic alliances with influential Roman leaders, notably Julius Caesar and Mark Antony, bolstered her reign and extended Egypt’s autonomy. Cleopatra’s enigmatic persona and tragic fate continue to captivate the imagination of people across the globe.
In addition to her political acumen, Cleopatra VII was a patron of the arts and sciences. Her court was a center of intellectual exchange, supporting scholars, artists, and philosophers. She contributed to the preservation of ancient Egyptian culture and knowledge while also embracing the fusion of Egyptian and Hellenistic cultures. Her patronage fostered a renaissance of sorts in the arts and academia.
6. Thutmose III (1479-1425 BCE)
The Warrior Pharaoh


Thutmose III, often hailed as the “Napoleon of Ancient Egypt,” expanded the Egyptian empire through a series of triumphant military campaigns. As the sixth Pharaoh of the 18th dynasty, his reign witnessed numerous conquests, strategic alliances, and significant territorial expansions, cementing Egypt’s dominance in the region.
In addition to his military conquests, Thutmose III was an adept administrator and innovator. He implemented efficient administrative reforms that strengthened Egypt’s governance and established a system of tribute collection, ensuring the kingdom’s financial stability. Thutmose III’s administrative advancements laid the groundwork for efficient centralized rule.
7. Akhenaten (1353-1336 BCE)
The Sun King


Akhenaten, also known as Amenhotep IV, pursued radical religious reforms during his reign in the 18th dynasty. He introduced a monotheistic cult centered around the sun god Aten, shifting from traditional polytheism. His distinctive artistic style and the establishment of a new capital city, Amarna, mark a significant cultural and religious shift during ancient Egyptian history.
Akhenaten’s reign also witnessed artistic innovation and a departure from traditional artistic conventions. The distinctive art during his rule, characterized by elongated figures and a focus on naturalistic depictions, reflected the religious revolution he initiated. The artistic style under Akhenaten’s rule stands out as a unique and influential period in ancient Egyptian art history.
Also Read : 5 Weird Facts About Ancient Egypt
Conclusion :
The Pharaohs of Ancient Egypt stand as enduring symbols of power, innovation, and cultural richness. Their remarkable achievements, architectural marvels, and contributions to civilization continue to captivate and inspire generations. Exploring the legacies of these seven captivating Pharaohs provides a glimpse into a civilization that shaped human history, leaving an indelible mark on the world.